9. High-tech Jobs vs Low-tech Jobs. As the economic stats on China and the US show
below, 90% of the jobs in China and the US are not in big corporations but in "low-tech"
small and medium enterprises (SMEs). It is also these low-tech SMEs which have witnessed
quasi uninterrupted revenue and job growth since the oil shocks of 1973 and 1979 and
numerous recessions which followed. By contrast, most of the tens of millions of jobs lost
since then, over the last 70 years, when the US transitioned itself out of heavy industry,
have come from the big corporations, In fact, the buzz around AI has provided the ideal
excuse for the "high-tech" giants (Meta, Amazon, Microsoft, Google, Intel, Accenture,...)
to lay off tens of thousands of their workforce.
In spite of government policy favoring Big Business, these small, low-tech businesses have
continued to show remarkably resilient entrepreneurship. These small businesses, with
less than 500 employees, account for 40% of US GDP to the big corporations' 60%.
The real challenge ahead, which the Chinese have apparently understood judging by their
2024 economic report below, is to channel significantly more of our still enormous wealth
into helping small businesses achieve stable and sustainable growth at home and abroad.
Google Keynote May 2025 Gemini Enterprise October 2025
AI Disruptor
AI Disruptor
Competitive Advantage
The Strategies
Product, Market, Channel
see NFTs Case Study
Market
(Marketing Strategy
4 Ps)
THE FIT
Product/
Market/
Channel
THE STRATEGY
Differentiation (Scope)
THE POSITIONING
Higher, Mid or Lower-end Market Positioning
MARKET FORCES
Product Life Cycle
DIFFERENTIATED
PRODUCT
OpenAI ChatGPT chatbot
PEOPLE
Customer Satisfaction
Industry
(Competitive Strategy
5-Forces)
THE FIT
Service Model/
Deployment Model/
Revenue Model
THE STRATEGY
Standardization (Scale)
THE POSITIONING
Quality, Cost or Niche
Industry Positioning
MARKET FORCES
Industry Structure,
Capital Markets
SCALED
PRODUCT
AI LLM Standard
PEOPLE
Job Description
Firm
(Business Strategy)
THE FIT
Customers/
Value Chain Partners/
Employees
THE STRATEGY
Innovation (Strengths)
THE POSITIONING
Technology Leader or Follower
Firm Positioning
MARKET FORCES
Business Cycle
CORE
PRODUCT
OpenAI ChatGPT 4.5
PEOPLE
Functional Description
INTERNET NETWORK
LANGUAGES
CLOUD OF THINGS
DATA
OPERATING
SYSTEMS
CLOUD SOFTWARE
SECURITY SOFTWARE
NETWORK SOFTWARE
APPLICATION SOFTWARE
HARDWARE
& RELATED
SOFTWARE
DATA ANALYST
APPLICATION DEVELOPER
ANALYTICS & BI
EXPERIENCE
DESIGNER

SHARED WORKSPACE
WORKFLOW
ERP
DIGITAL CURRENCIES
MARTECH
Competitive Strategies
OPEN SOURCE FRAMEWORK
EXPERIENCE DESIGN
STANDARDS
DEVELOPER TOOLS
DIGITAL EDUCATION
Social Media & eCommerce
TELCOS (MSOs)
DATA CENTER OPERATORS
WEB PLATFORMS
Market Disruptor
Market Challenger
Market Incumbent
Market Follower
Industry Analysis
HARDWARE & SOFTWARE
See also The Internet page
The Chinese AI User Platform
Table of Contents
The Strategy Process
applied to the AI market
The Product:
1. Industry Analysis
The Product/Market/Channel Fit:
2. Market Disruptor Strategy
3. Market Challenger Strategy
4. Market Incumbent Strategy
5. Market Follower Strategy
6. Business Models
7. China
8. DeepSeek
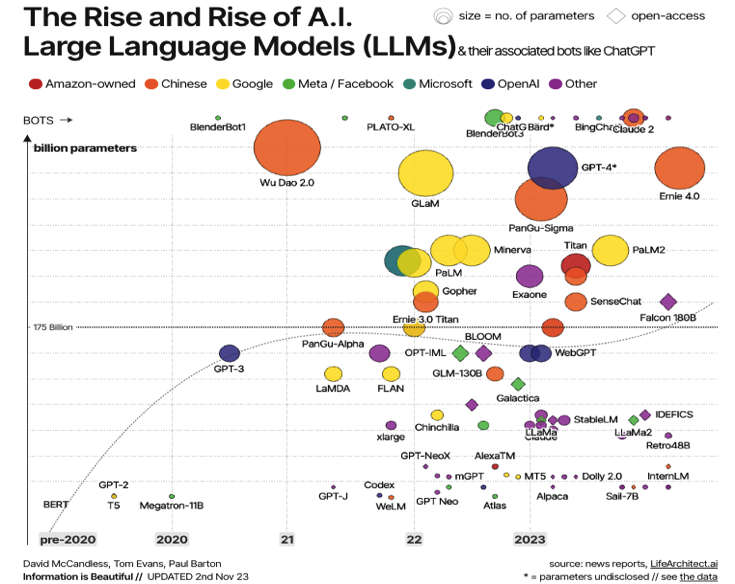
6. Business Models. Then only, after reviewing their respective competitive strategies,
do they develop their business models. The map below, shows who the biggest players
are, as reflected by the size of the circles (Open AI in purple, Google in yellow and
the Chinese in orange), operating their AI data centers powered by their AI chips and
AI databases and running their AI engines. So far, as their own chips are still under
development, only Nvidia GPU chips are used.
Perhaps more importantly, the map also tells us what their distinct business models
would be. To begin with, using the 4 Ps, in terms of the Product, they are tailoring
and pricing their software, the AI engines, to meet the needs of their target markets.
For example, Google has on the one hand their top line Vertex AI LLM, priced higher
to process resource-intensive apps for those of their Fortune 500 customers needing
not just text but images and videos and on the other hand, their Coden, Imagen, and
Chirp LLMs, which are customized into more narrowly defined apps and priced lower.
In terms of the remaining 3 Ps, Price, Place and Promotion, nothing has changed.
They will continue to use dual pricing, billing a fixed subscription fee and a variable
usage fee, based on the number and complexity of the queries known as tokens. As
for the marketing channel downstream, because they target the entire total addressable
market or TAM, they will partner with the usual intermediaries, the wholesalers and
the retailers. We will therefore continue to have a Kyndryl, an IBM spinoff, to operate
the data centers under the AIOps moniker and IBM itself to provide the higher margin installation services using the watsonx and Granite portfolio of AI tools. Just as they did
with the Cloud and the Web, these IT service providers would offer to "integrate"
this time around the latest craze, AI, into our IT systems.
5. Market Follower Strategy. It is only after reviewing the competitive landscape
and the competitive strategies of those who are in fact the market leaders (Open AI,
xAi, Google as showcased above) that one can begin to tackle one's own strategic
review as a market follower. As shown below, the firm has to find the right product/ market/channel fit. Using such tools as the 4 Ps and the 5-Forces, it must develop
not one but 3 strategies, its business, competitive, and marketing strategies, by iteration.
The Chinese upstarts, not only DeepSeek but now also 01.AI, Minimax M1, Moonshot
AI, Zhipu AI, Baichuan Intelligence and Stepfun, could be such market followers.
They are backed by China's own FAANGs, Alibaba, Tencent, Baidu and the Chinese
government.
4. Market Incumbent Strategy. OpenAI backed by Microsoft, Anthropic backed by
Amazon, and xAI backed by Elon must face off the most formidable incumbent that
is Google. As shown in the 2-hour-long video of its 2025 Keynote below, the search
giant has made great strides, having nearly finished making end-user tools which the 3
upstarts do not yet have. To go against OpenAI's AI engine ChatGPT, Anthropic's Claude,
and xAI's Grok, Google must have easily matched the 3 upstarts' $10B to $15B of capital commitments, in order to develop and roll out its own AI engine, Google Gemini.
To understand the extent of Google's formidable reach, let us not forget that the founders
of OpenAI, Anthropic and now Safe Superintelligence, Inc (SSI) cut their teeth in their
twenties as crack developers at Google's in-house AI incubator, Google Brain (notably Ilya
Sutskever, later chief scientist at OpenAI and after a falling out with Sam Altman now at
his own firm, Safe Superintelligence, and the Amodei siblings at Anthropic).
However one wants to cut it, the Internet business we've now rebranded as AI is still
Google's "sort and search" business extended now as a "sort, search, and solve" business.
As of mid-2025, we can do search in "AI mode" on Google's website.
How We Do It
Strategy
How We Conduct A Strategic Review
1 The Strategic Review applied to the AI market
We conduct 3 reviews: a strategic review as shown on this page, and a business and an
operational review as shown on the following page.
Depending on whether the firm is a market disruptor, market challenger, market
incumbent or market follower, the strategic review is conducted as follows:
1. Industry Analysis. The strategic review always begins with an industry analysis. In the
IT industry, almost like clockwork, a new market disruptor emerges every ten years.
Today, that disruptor is of course OpenAI.
2. Market Disruptor Strategy. Here too, the strategic review does not begin with your
firm's business strategy but with that of the market disruptor, namely OpenAI. It
consists of the following phases:
. Initial Product. 10 years on after its founding in 2015, OpenAI has successfully come up
with a marketable product, comprised of a program (the large-language model or LLM),
a database covering everything publishable online (GPT), and a chatbot (ChatGPT).
This first phase can be called the core product development or just product phase
. Go-To-Market Financing. It successfully clinched already in 2019 $1B from Microsoft
to finance its product development. Killing two birds with one stone, by 2023 it received
another $12B from them to finance its commercial development which enabled it
at the same time to tap into Microsoft's customer base of 1.6B users and 2M businesses.
This second phase can be called the go-to-market product financing or money phase
. Standards. As in any industry, the 3 to 5 major players (OpenAI, Anthropic, Meta,
Google, DeepSeek) must agree on an industry-wide standard, which is the only way
for individual firms to benefit from economies of scale and bring down costs. This is
why OpenAI and Anthropic are pushing to have their LLM models, respectively
o3 and MCP, adopted as the standard for AI, just as Linux became the standard
for operating systems, and distribute it at first for free to lure the greatest number of users.
This third phase can be called the scaled product development or industry phase
. Partnerships. OpenAI has recently acquired for $6.5B Jony Ive's design firm iO, in
order to fill a missing gap in hardware, and this time to lure the greatest number of buyers.
This fourth phase can be called the differentiated product development or market phase
. End-User Product. User applications, called agents (hence the term "Agentic AI"), must now be
scaled up. This fifth phase can be called the application development or monetization phase
3. Market Challenger Strategy. A challenger to watch closely is Elon Musk's xAI. Just
as Apple was also a challenger until it bypassed in a few short years Blackberry, Elon has
very quickly narrowed OpenAI's lead i) by releasing the right products in his Grok AI engine,
his AI chip for his Dojo supercomputer and Colossus data center, ii) by tapping into
the right market of 1.6B users, iii) through the right channels at X and now at Telegram.
Investors, who have put in $27B, have seen xAi's valuation increase 8-fold to $200B in a year
China Economic Stats US Economic Stats
(State of the Economy) (Breakdown of SMEs vs Big Business)


The Chinese AI Infrastructure
To contact us
Or Man Partners
7. China. Finally there is the biggest threat of all, China. As we saw above with the
top US market leaders, the 3 critical success factors are i) the product's software
(AI engine), and hardware (AI chip), ii) the market's billion+ users (AI apps using AI
agents as middleware to adjust the application user interface or API), and iii) the money.
China fulfills all 3 criteria but unlike us, without neither overvaluing nor overleveraging.
On the software side, the top Chinese Internet companies, such as Alibaba, Tencent,
Baidu, and an OpenAI clone, DeepSeek, are already at the 3rd version of their AI
engines, respectively Qwen 3, HPI, Ernie 4.5 and DeepSeek.
On the hardware side, Huawei holds 80% of the AI infrastructure market, equipping
its Mindspore chip software to run its Ascend 910D (and by 2027 its 920 AI quantum
computing chip) on its 245 TB OceanDisk EX 560 solid state hard disk.
On the user side, it is again Huawei who provides both the Harmony OS software and
its Kirin 9020 chip, both of which power its family of Mate smartphones and its car
systems for its co-branded EVs. Kingsoft's WPS Office, which runs not only on
Harmony OS but also on Windows, OS, Android, and Linux, and which moreover
is written in our Delphi/C/C++ programming languages, now competes head on
against Microsoft Office. Should we not move to Harmony OS as well?
The Money. Then there is the invisible hand of the Chinese government. As it has
done with EVs, it has already shelled out this year alone some $60B of subsidies to
the Chinese IT industry (our governments have also subsidized as much but without
any strings attached, throwing good money after bad).
The Brainpower. That the Trump Administration has pushed forward its $500B
Stargate project with Oracle, OpenAI and Softbank and forced Apple to manufacture
at home is a good sign. The question now is how the US will train 4 to 5 times more
than the 140k engineers it currently trains to catch up to the 1.4M engineers the
Chinese churn out every year.
8. DeepSeek, Moore Threads, Humanoid Globala. Have you heard of these firms?
The first video below is a profile of DeepSeek's founder, Liang Wenfeng, a
multi-talented entrepreneur who, after completing his master's in computer science
in 2010, developed already back then an AI stock-trading program to take advantage
of the capital markets' instability and volatility after the 2008 GFC. Capitalizing on its
success, he created his own hedge fund, raising up to 19B yuan. In a sense, Liang
was already stress testing what was to become DeepSeek. He applied it to the most
difficult usecase there was, using the same type of AI algorithmic trading we had
at home, to invest in the Chinese stock market for his clients.
It therefore came as no surprise that Liang took a step further in 2019 by founding
High Flyer AI to develop what was to become DeepSeek. When the first R1 version
of DeepSeek was rolled out in January 2025, upon learning that its development
had cost a mere $6M compared to the tens of billions of dollars raised by OpenAI,
US tech stocks tumbled, losing $1T in market value.
The second video profiles Moore Threads, a Chinese start-up which was oversubscribed
more than 4 000 times for up to more than the market cap of Nvidia or $4T. It makes
GPUs to rival Nvidia. Then there is Humanoid Global, a Chinese VC fund with backing
from Amazon, Google, and again looming large, the Chinese government, which invests
in humonoid robotics, which can replace with lights out humans 24/7, 350 days a year non-stop.